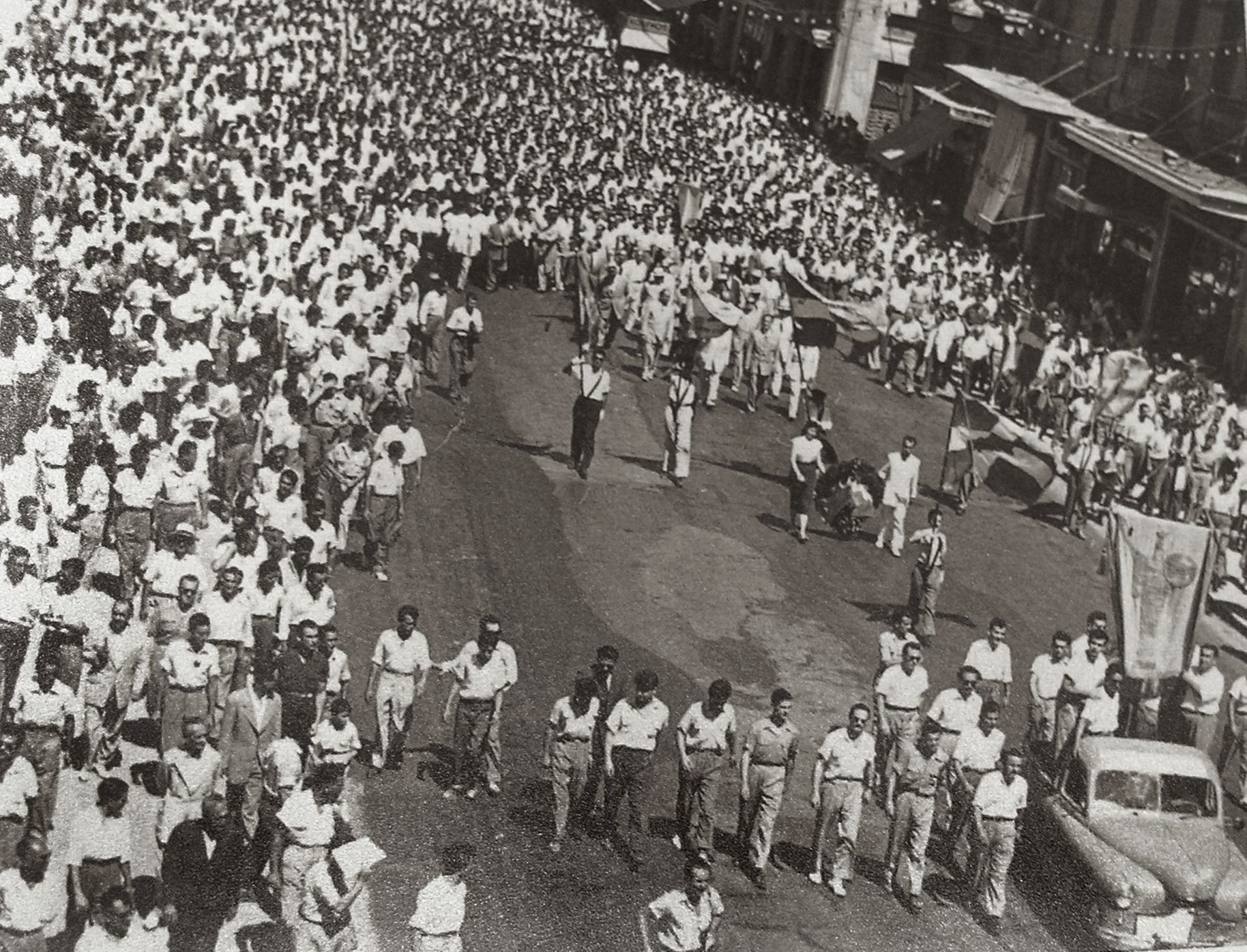
Research and Welfare
The University of Athens has always been identified as a center of continuous scientific research and study. Cognitive divisions, scientific fields, and innovative teaching methods were initiated in its curriculum. As an institution, it contributed decisively to solidifying within the scientific community all the practices and methods that were formulated during the establishing procedures and further expanding their dominion. Modern educational practices were developed within its framework shortly after being implemented in universities in the West, such as laboratories and study rooms. The University has been in a constant dialogue with higher education entities abroad, starting with the early participation of its faculty in international conferences and continuing to the European student exchange program ERASMUS. At the same time, a large part of the institution's endeavors addressed society's needs. The University of Athens developed and continues to develop remarkable work in the area of welfare and healthcare , from the Astykliniki (City Clinic) of the 19th century to the current undertakings at the university hospitals and the refugee programs..
The satirical poet Georgios Souris.
Fasoulis*, a graduate of Philosophy,
Was examined two years ago in Physics,
All at once in solids, gases, and liquids,
in the Voltaic and the Wollaston piles,
in the refraction of the optical ray,
and in the well-known pot discovered by Papinos,
in the positive and in the negative electricity as well,
he so brilliantly answered so many questions,
That I begged him with very courteous words
to take the exams in Physics one more time (...)
And for this reason, I am issuing this certificate...
Stroumpos, well-known Professor of Physics.
Georgios Souris, Fasoulis's studies.
From "ΑΠΑΝΤΑ" (Collected Works) by Georgios Souris, Vivliothiki gia olous(Library for all) Editions, Athens 1980.
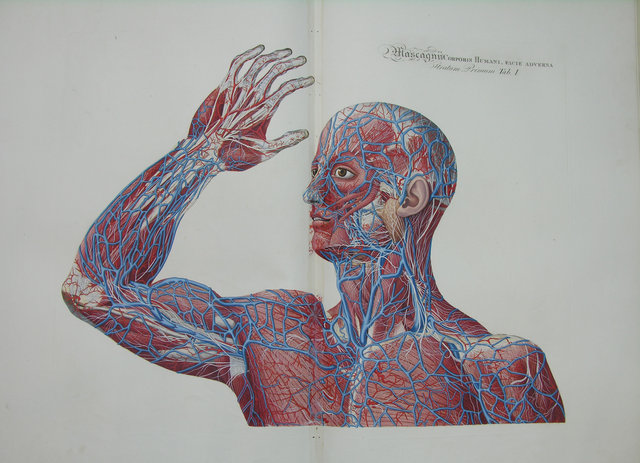
The Anatomy Atlas by the famous Italian anatomist Paolo Mascagni (1755-1815), an 1823 edition, was donated by Otto to the newly established University.
University of Athens History Museum
«Anatomy of the Human Body» by D. Mavrokordatos, 1836. The first textbook manual of Anatomy.
University of Athens History Museum.
Treatise on the Draft or Hexabiblos of Constantine Armenopoulos by Emilios Herzog, 1837.
University of Athens History Museum.
«Edward Gibbon History of Roman Law» by Emilios Herzog and P. Paparrigopoulos, Law School professors, 1840.
University of Athens History Museum.
«Toxicology» by Xavier Landerer, head pharmacist of King Otto and Professor of Chemistry and later Pharmacology, 1843.
University of Athens History Museum.
Press Publication of the speech of the first parliamentary Prime Minister and Minister of Education Ioannis Kolettis in the Parliament, in the context of the deliberation of October 5, 1845. Kolettis proposes the merging of the chairs of astronomy and physics and refers to the importance of the chair of Chemistry, pointing out characteristically: ''Chemistry examines great things, like the movement of bodies, which is done through that great power, which was found by a great philosopher, and which he found seating under a pear tree,'' Aion (Eon), October 10, 1845.
Library of the Hellenic Parliament.
Drawing Plans by Theophil Hansen for the construction of the Observatory on the Hill of the Nymphs. They were published in 1846 in the Newspaper «Allgemeine Bauzeitung» (1/2).
University of Athens History Museum.
Drawing Plans by Theophil Hansen for the construction of the Observatory on the Hill of the Nymphs. They were published in 1846 in the Newspaper «Allgemeine Bauzeitung» (1/2).
University of Athens History Museum.
The Ministry’s letter to the Rectorate of the “Othonian” University which approves Professor K. Schinas’ journey to Bonn for the Synod of Philologists, 1841.
Athens University Historical Archive.
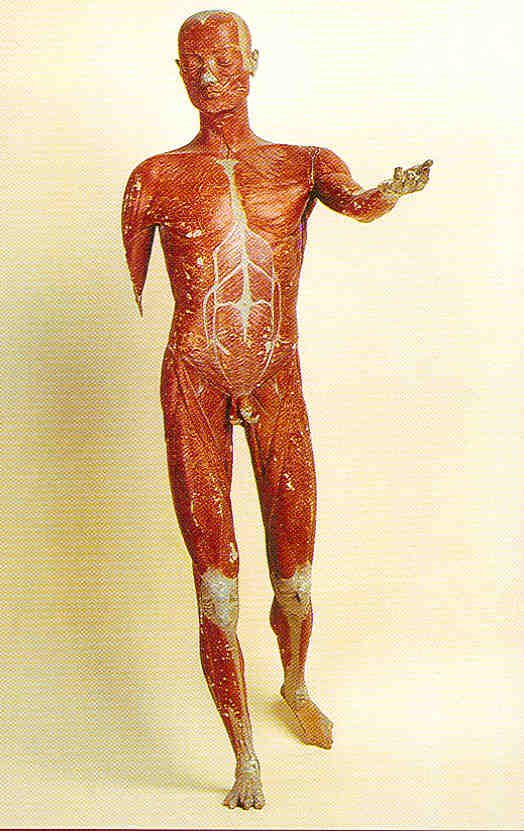
Figurine from the wooden figurine group of the Valsamakis Collection, which was used to demonstrate surface anatomy. They date back to the first half of the 19th century. The unique Valsamakis Collection consists mainly of wooden sculptures, wax casts, and scale models. Influenced by the famous anatomical wax models from Bologna, the Kefalonian doctor-philosopher Conte Konstantinos Valsamakis (b. 1780) oversaw the manufacturing of the Collection, which he brought from Florence, where he had studied and lived for a few years, to Argostoli. At the end of the 19th century, the Collection became the property of the University. The rest of the Collection, which numbers around 250 pieces, is stored in the Anatomy Museum of the University of Athens. The Athens University History Museum.
Athens University History Museum.
The Astykliniki (City Clinic), the first Day-Hospital of the University of Athens, 1923.
Historical Archive of the University of Athens / The Athens University: with its annexes, Athens 1923.
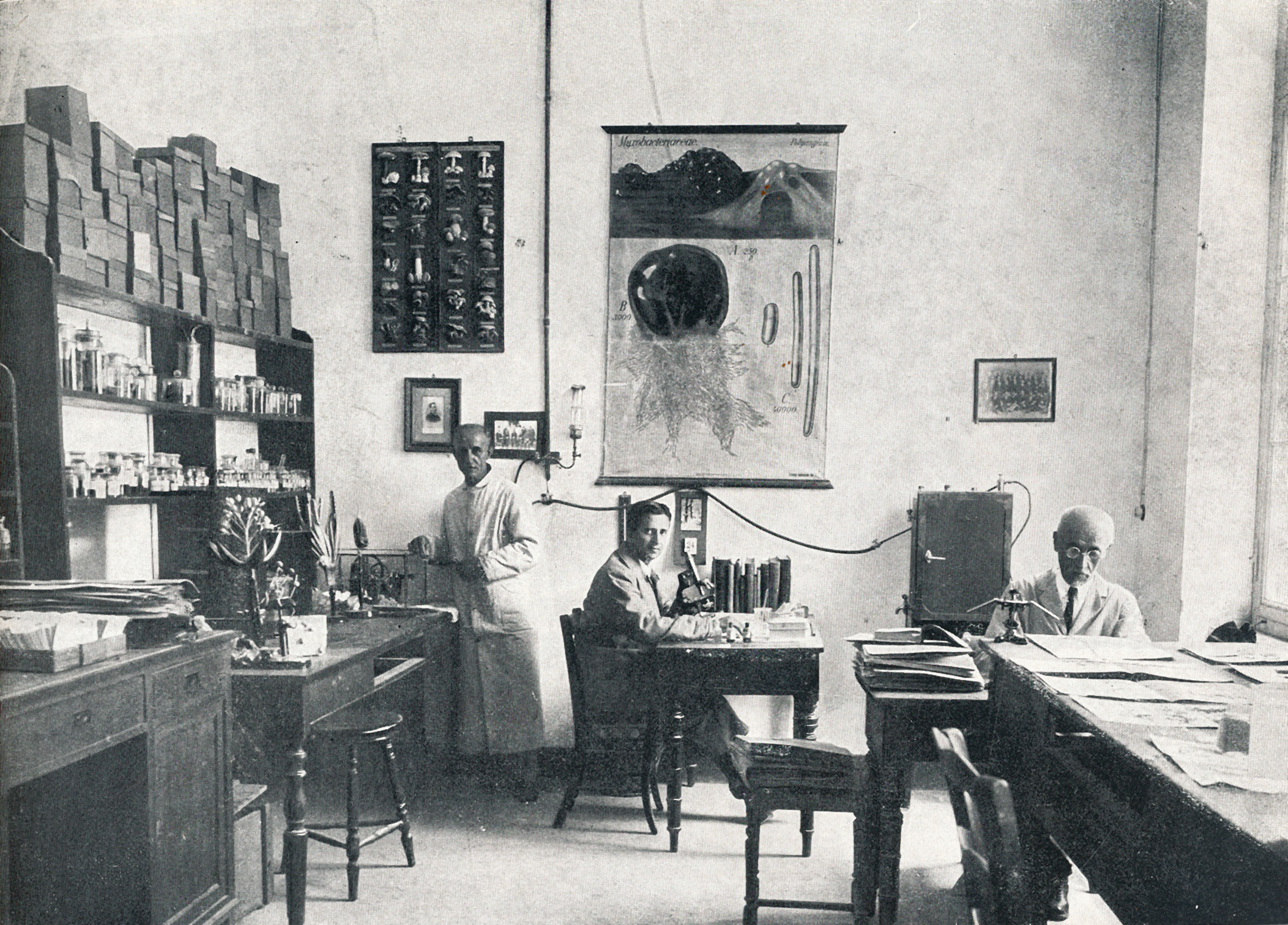
The Botany Laboratory of the University of Athens, 1923.
Historical Archive of the University of Athens / The Athens University: with its annexes, Athens 1923.
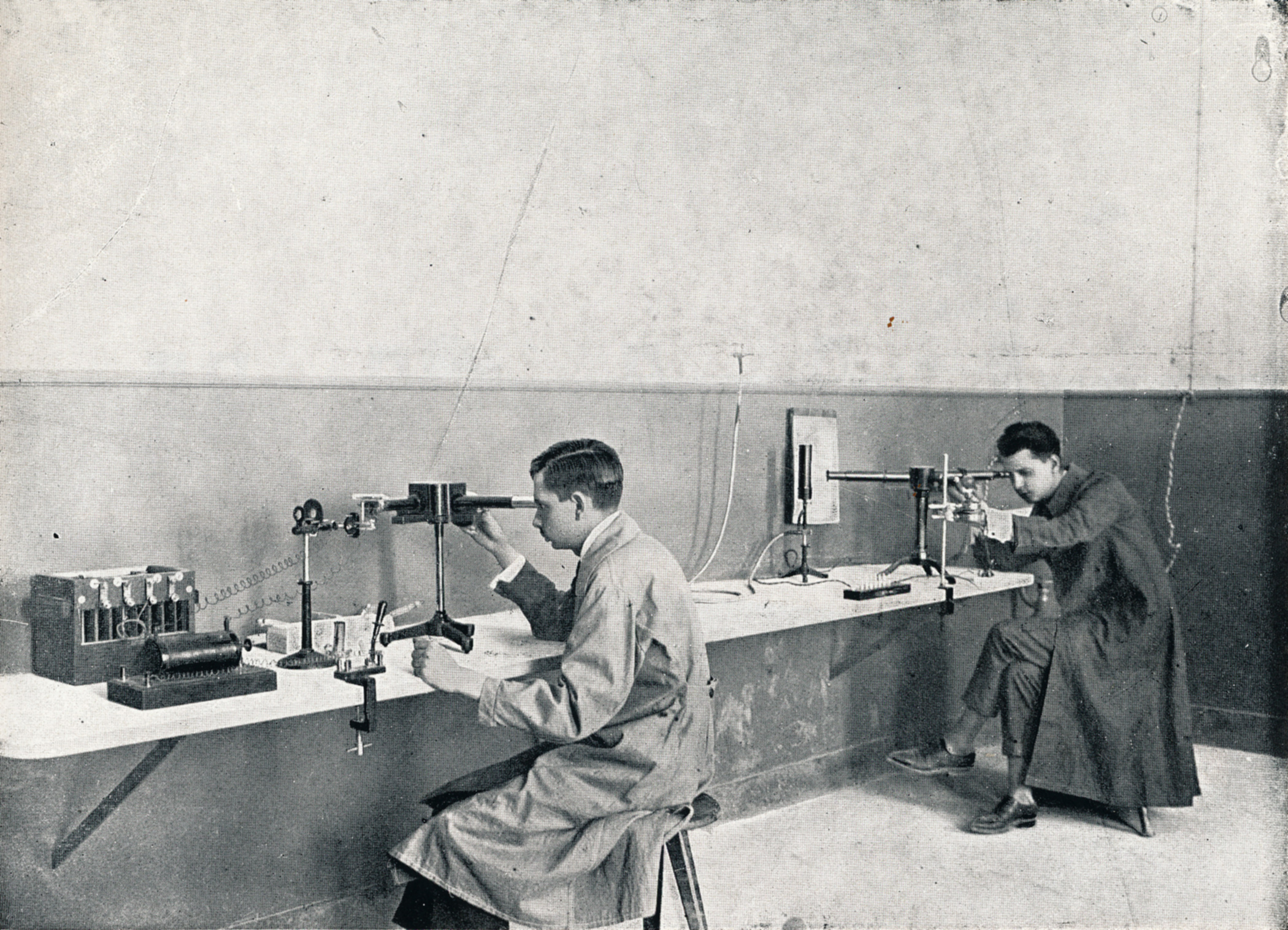
The Physics Laboratory of the University of Athens, 1923.
Historical Archive of the University of Athens / The Athens University: with its annexes, Athens 1923.
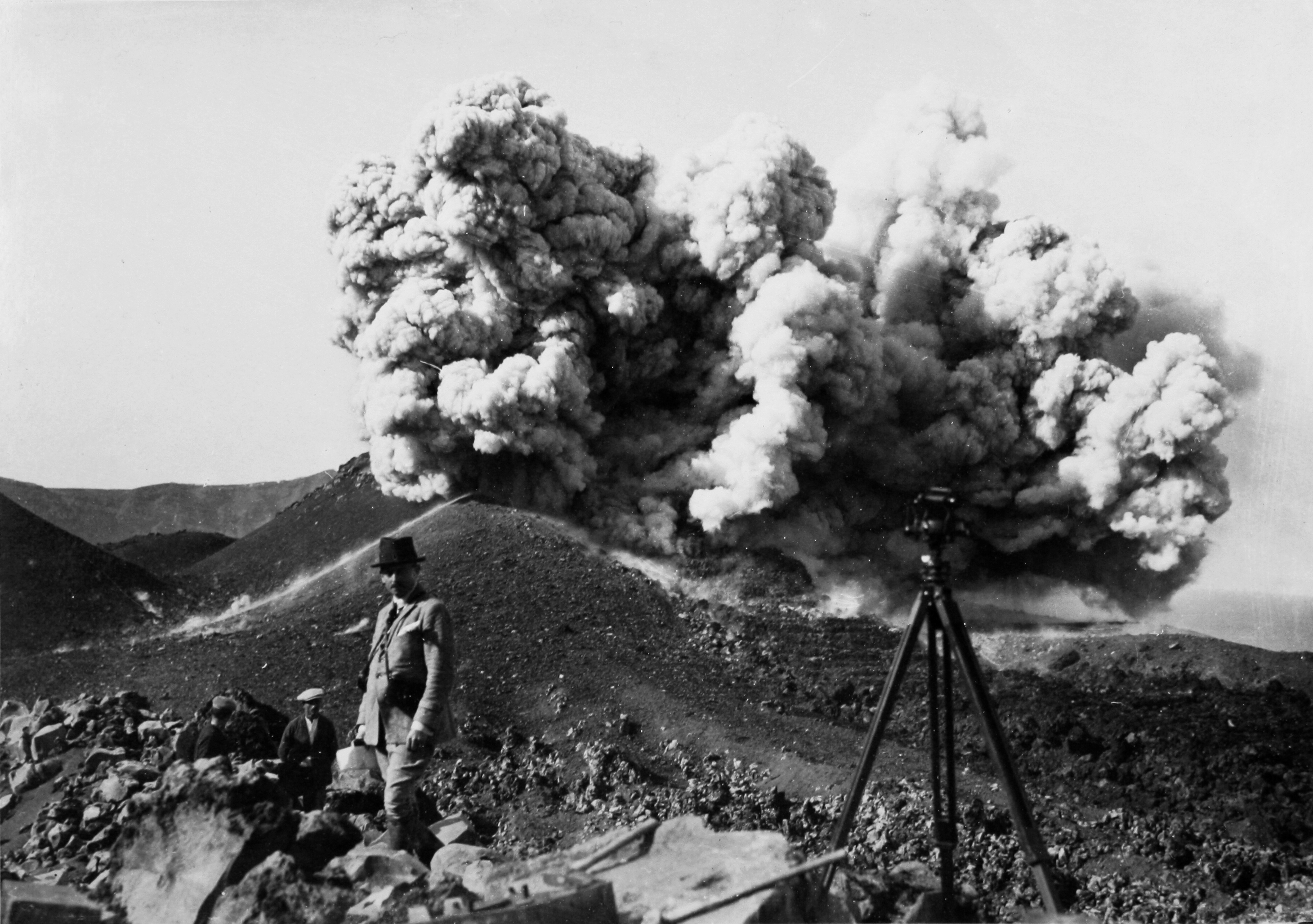
Professor of Mineralogy and Lithology K. Ktenas and, in the background, the then active crater of the Kameni volcano in Santorini, 1925.
University of Athens History Museum.
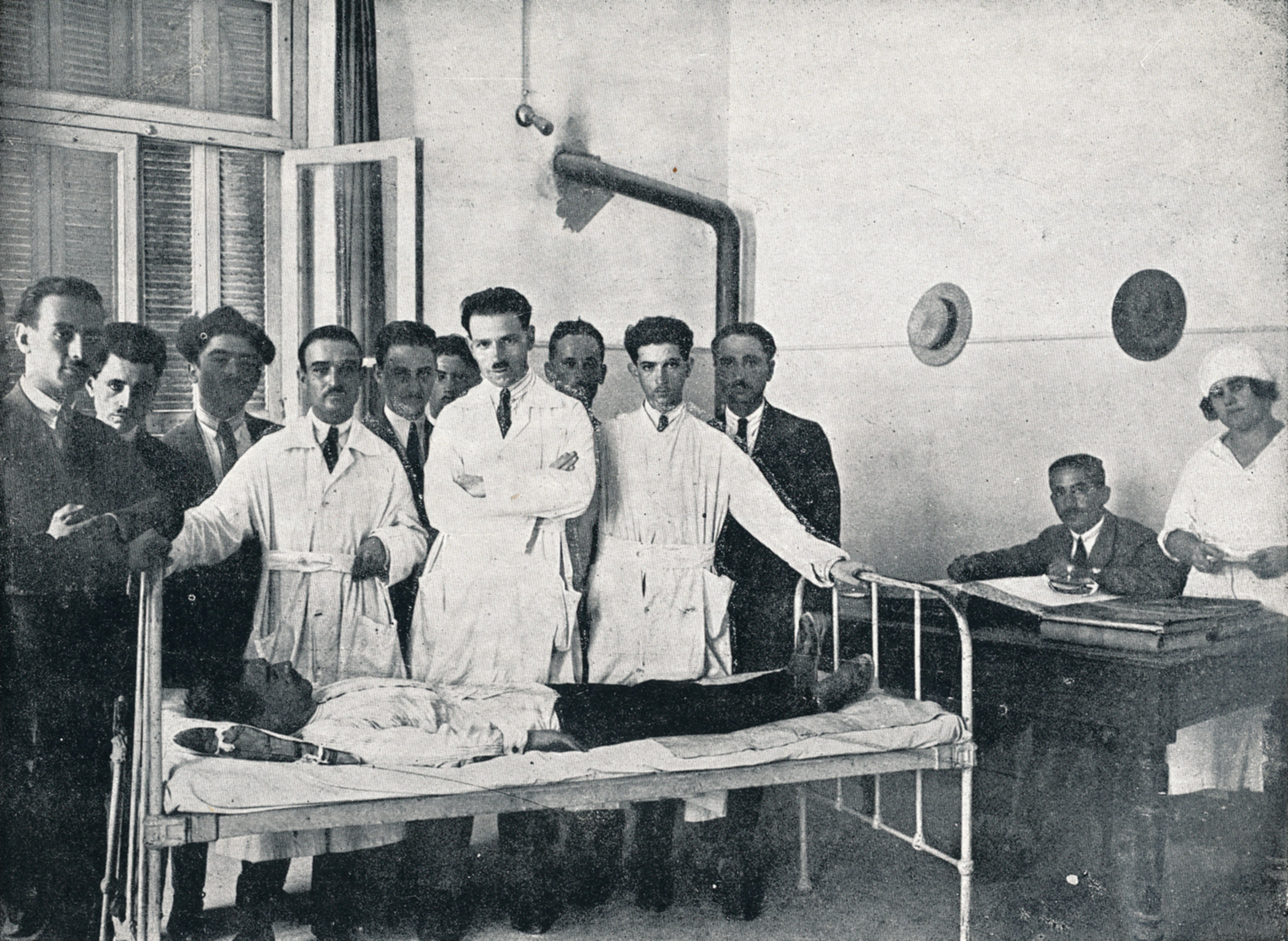
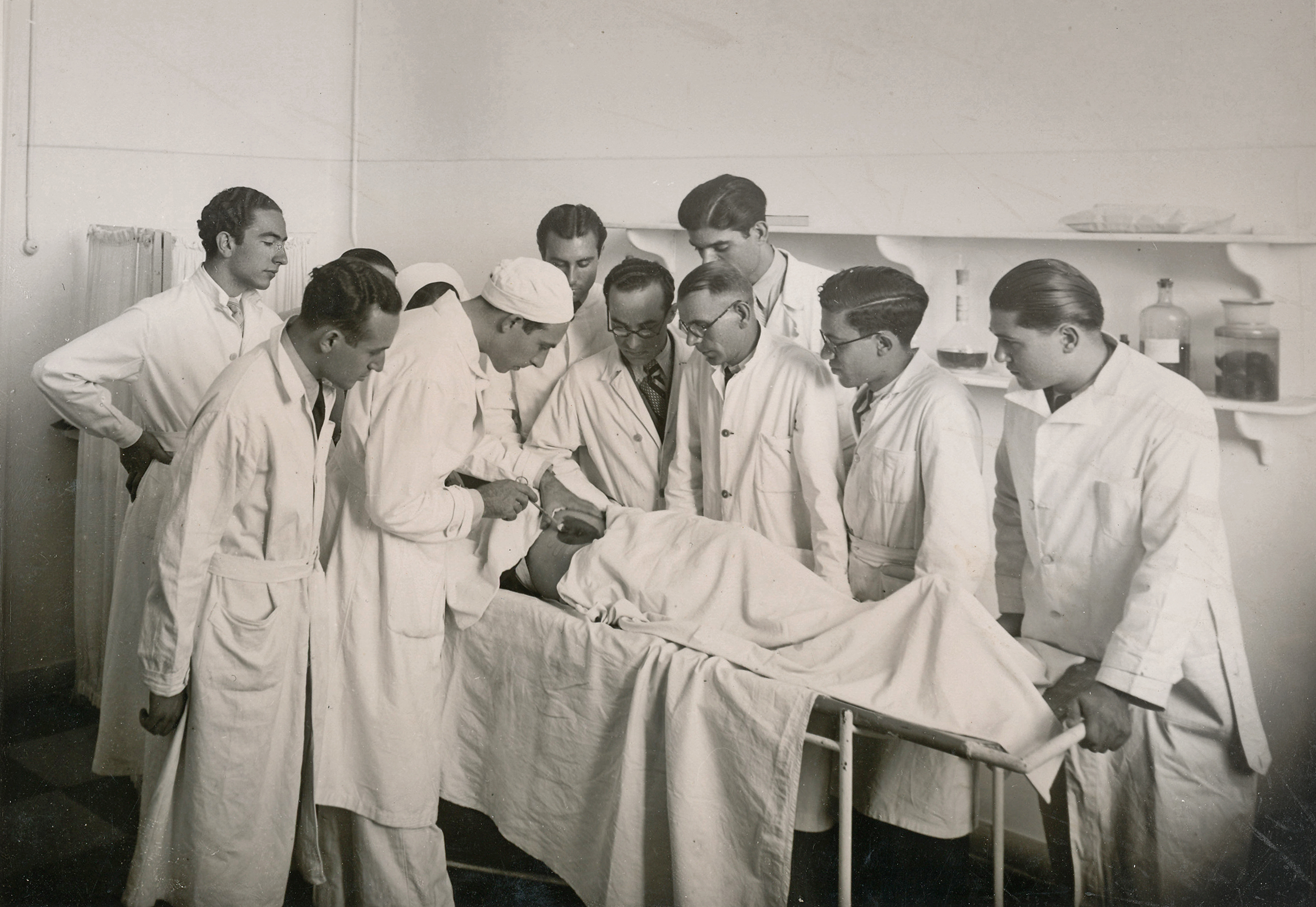
Treatment of a patient in the presence of professors and students of the University's Medical School, 1920s.
University of Athens History Museum.
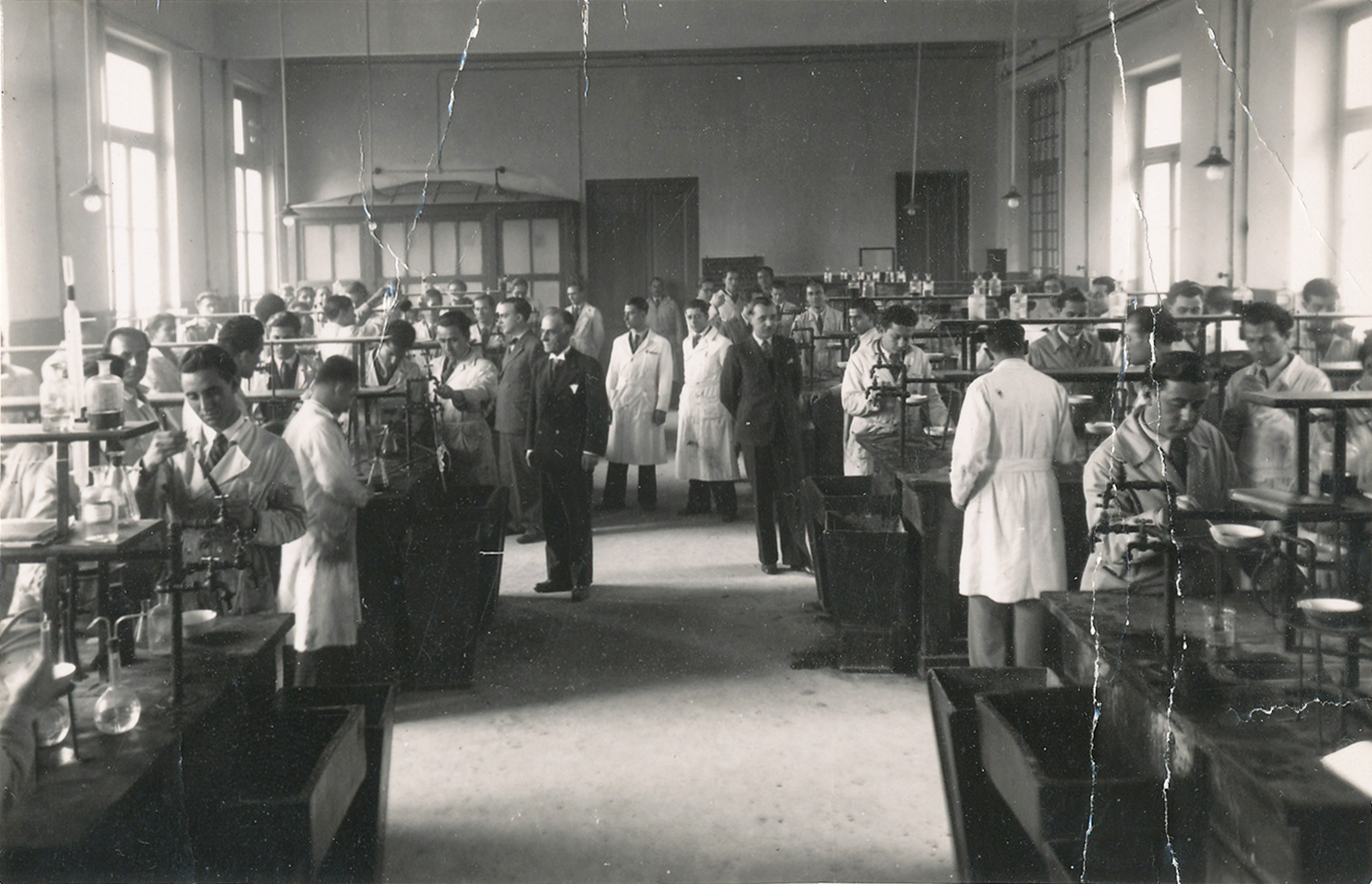
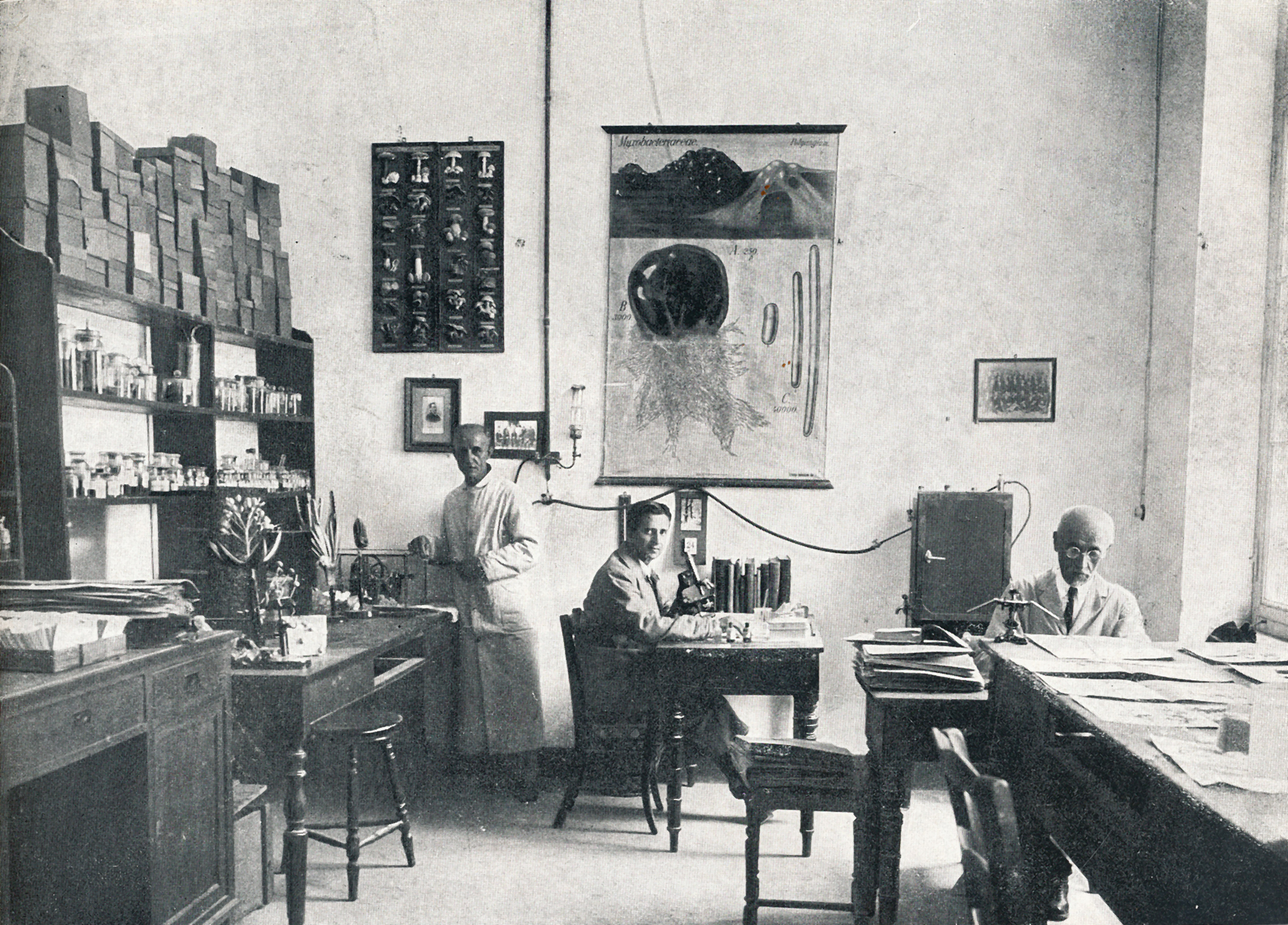
Exam room of the Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, 1930s.
Historical Archive of the University of Athens.
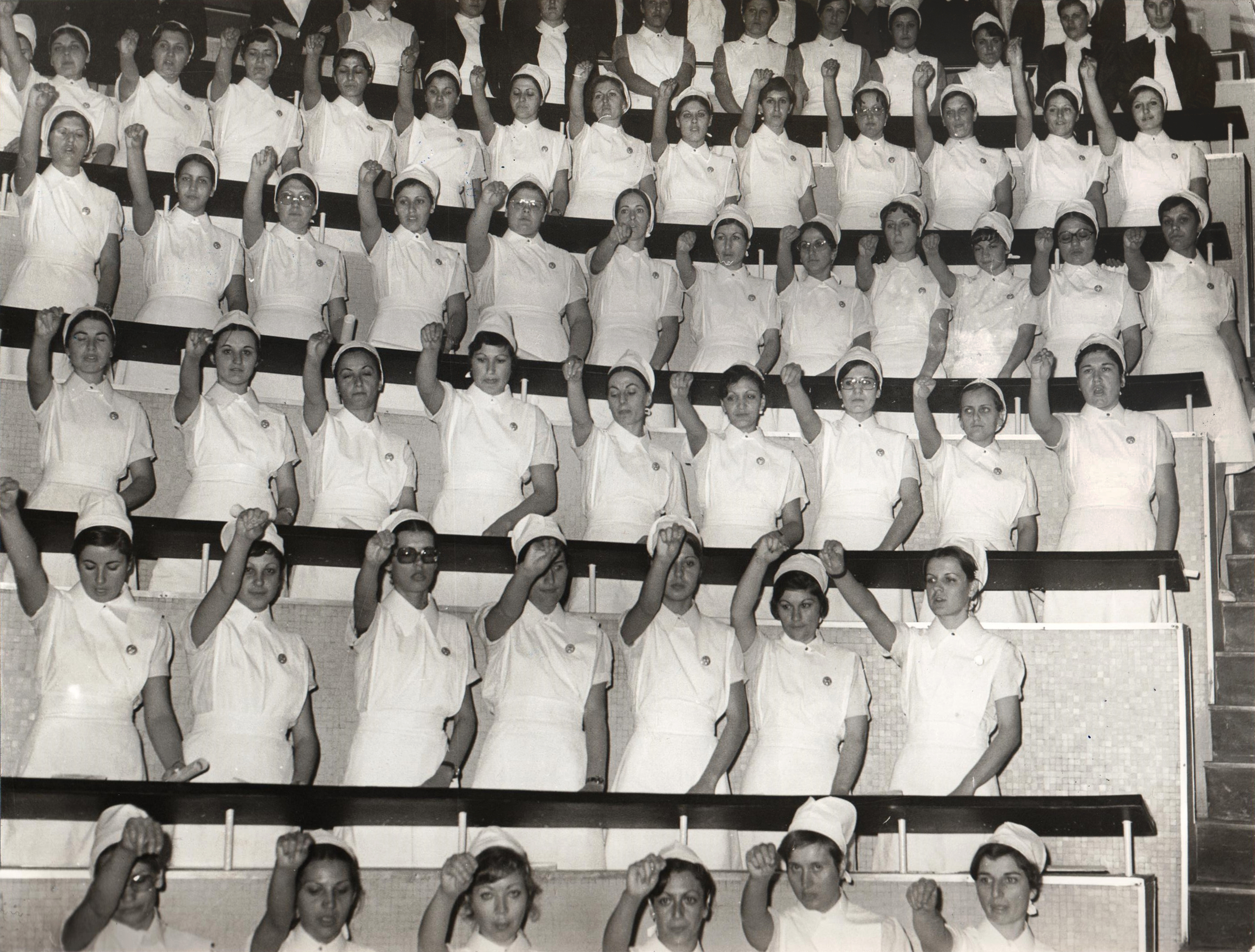
Group photo of the students at the School of Midwives of the University of Athens, 1950 - 1960.
Photographic Archive of G.N.A. «Alexandra».
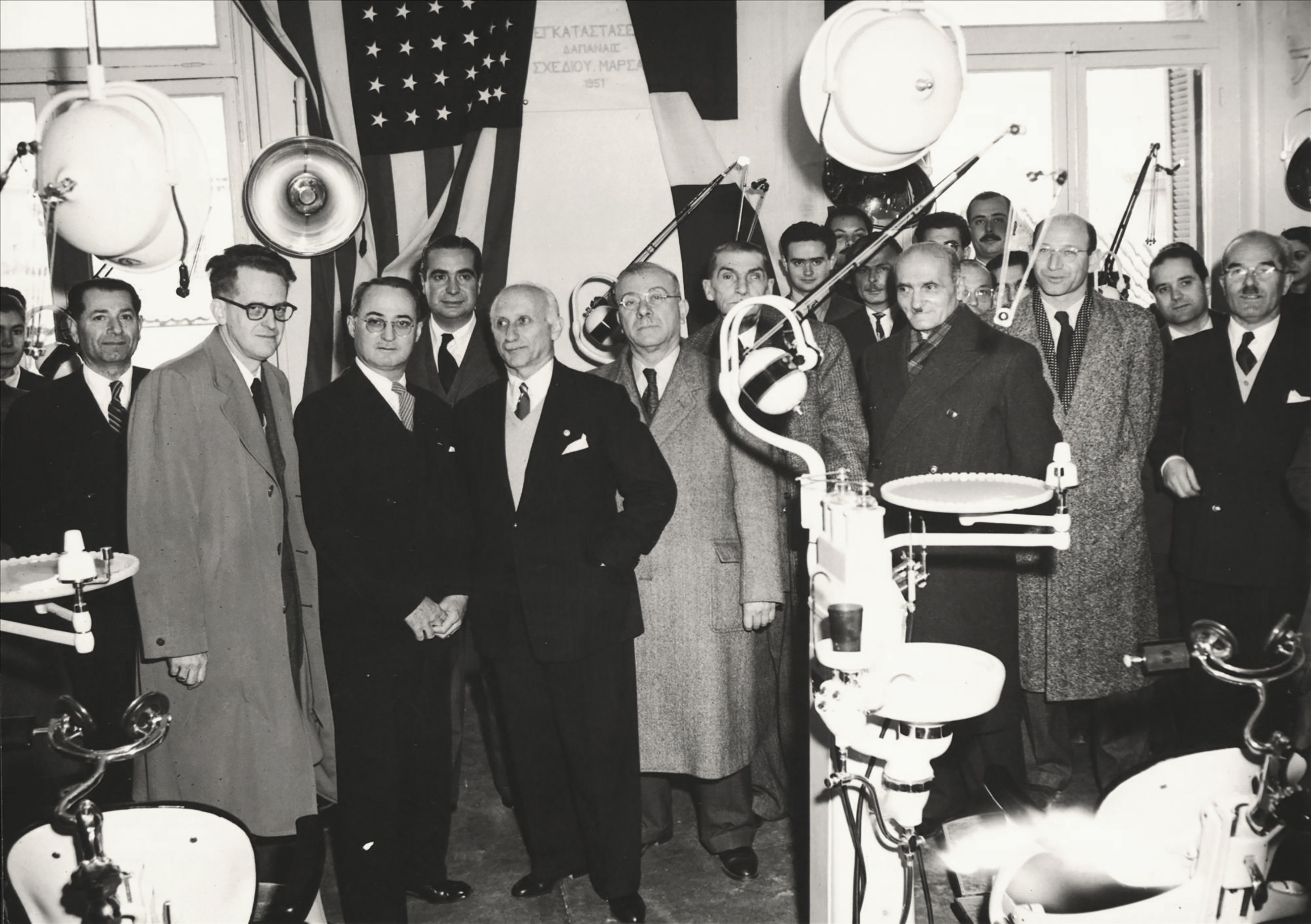
Inauguration of the new laboratories of the Dentistry School of the University of Athens, constructed with funds from the Marshall Plan, 1951.
Photographic Archive of MIET/ELIA.
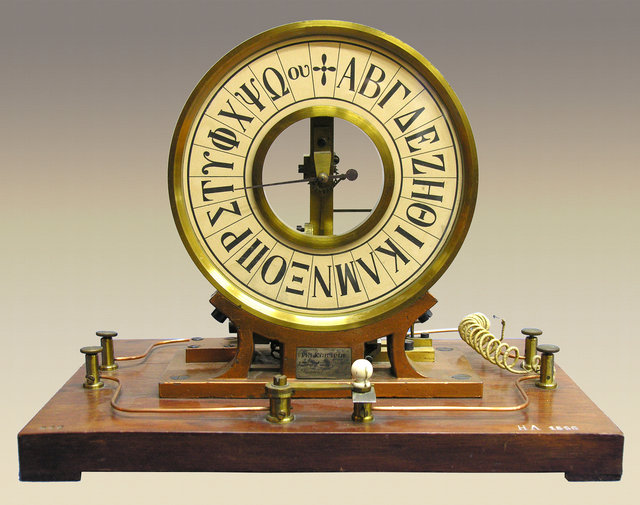
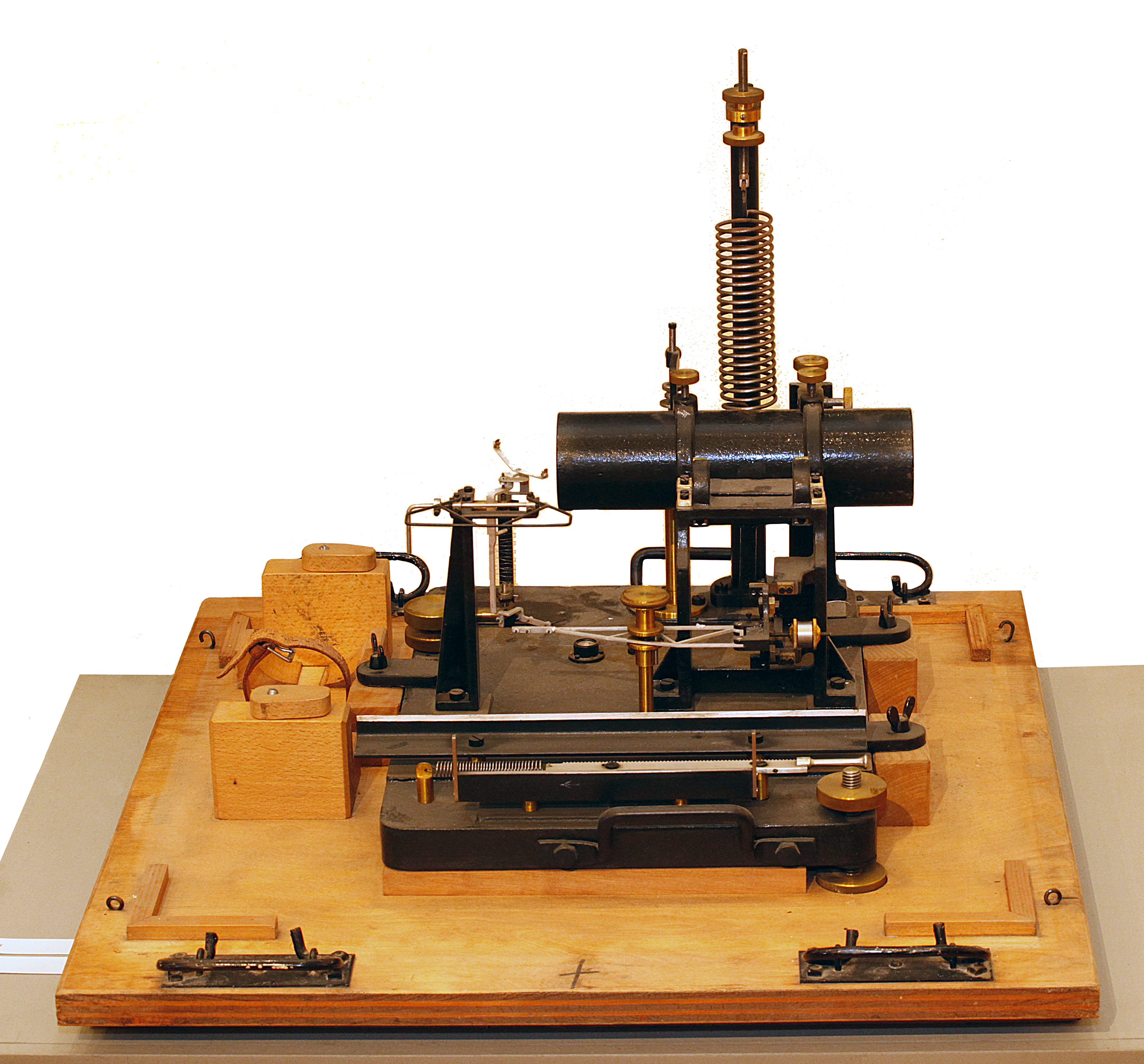
Receiver of alphabetical telegraph for educational use, 1850 – 1870. From the collections of the Old Chemistry Laboratory. Manufacturer: Paul-Gustave Froment, Paris.
Athens University History Museum.
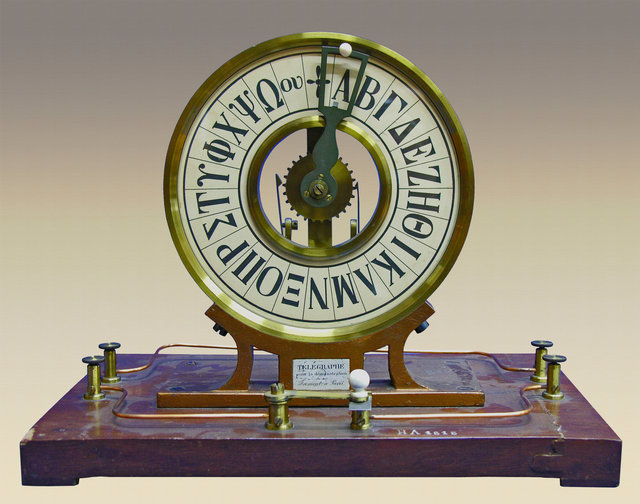
Alphabetical telegraphic transmitter for educational use, 1850 – 1870. From the collections of the Old Chemistry Laboratory. Manufacturer: Paul-Gustave Froment, Paris.
Athens University History Museum.
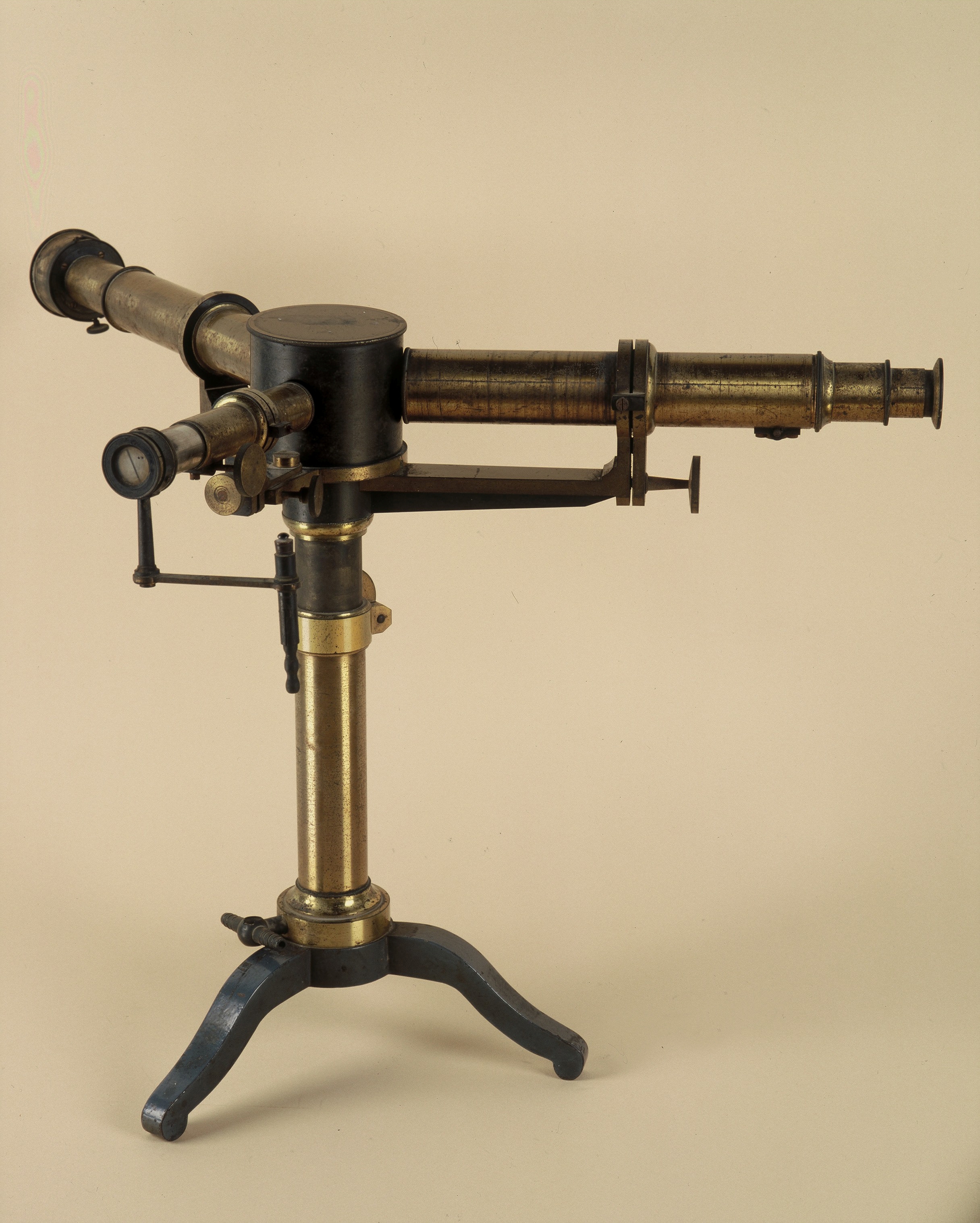
Spectroscope. Instrument of chemical analysis with the spectroscopy method, late 19th century. From the collections of the Old Chemistry Laboratory. Manufacturer: unknown (probably French made).
Athens University History Museum.
Educational galvanometer that can be converted into a compass and magnetometer, late 19th century. Manufacturer: Hartmann & Braun, Frankfurt, Germany.
Athens University History Museum.
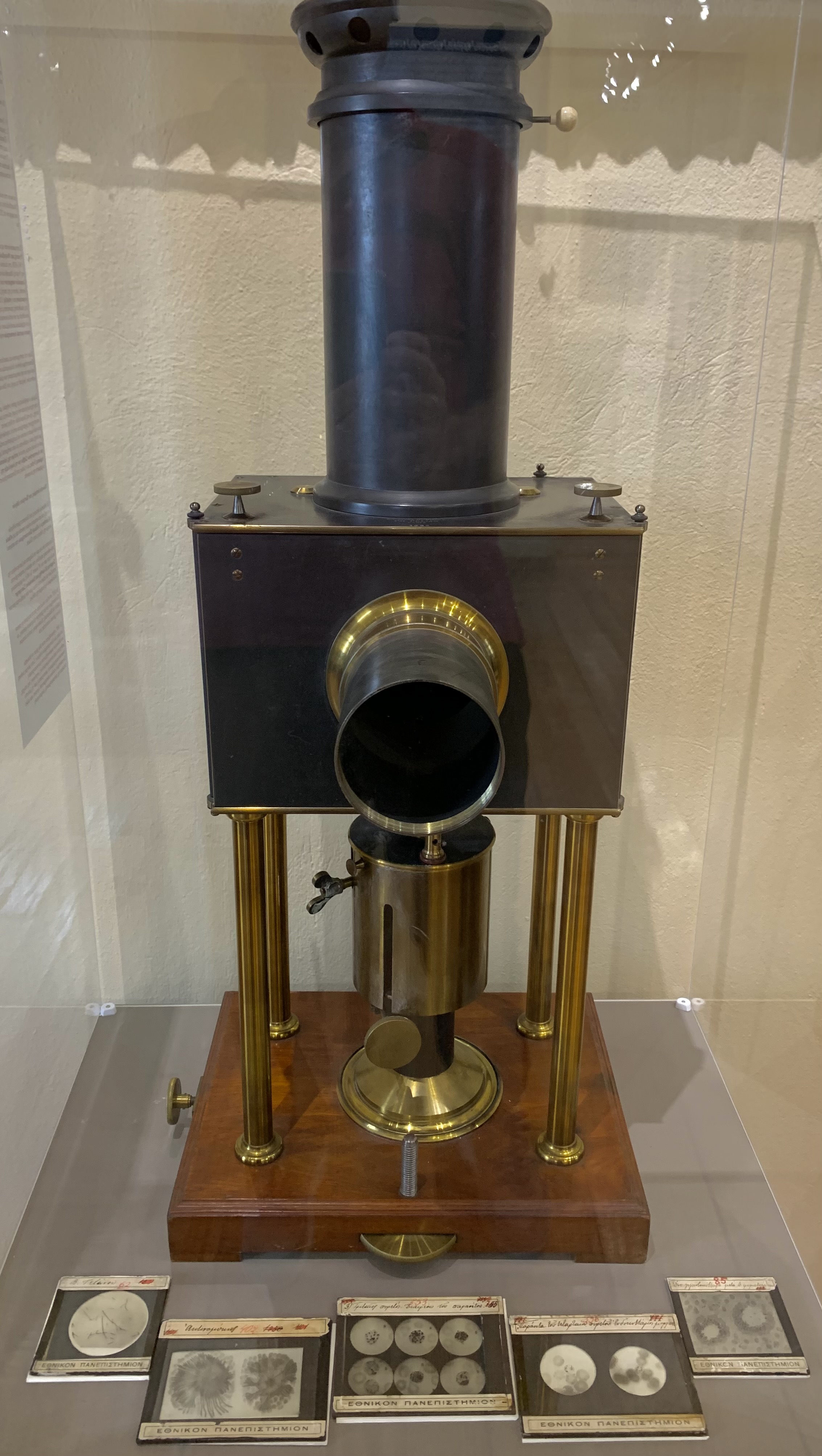
Projector. A scientific instrument for exhibiting visual experiments and projections of teaching material during the lecture course. The French Pellin House manufactured it in the late 19th century, and it belongs to the collection of the Old Chemistry Laboratory of the University of Athens.
The glass tiles belong to the collection of the archive of the Laboratory of Microbiology of the School of Health Sciences at the Athens University and concern 252 pieces measuring 8x8 cm. and 9x12 cm. In his Hygiene-Microbiology course, they were used as teaching equipment by the Professor of Hygiene and Microbiology, Konstantinos Savvas (1861-1929).
University of Athens History Museum.
Portable seismograph from the collections of the Seismology Laboratory, early 20th century. Manufacturer: Spindler & Hoyer, Göttingen, Germany.
Athens University History Museum.
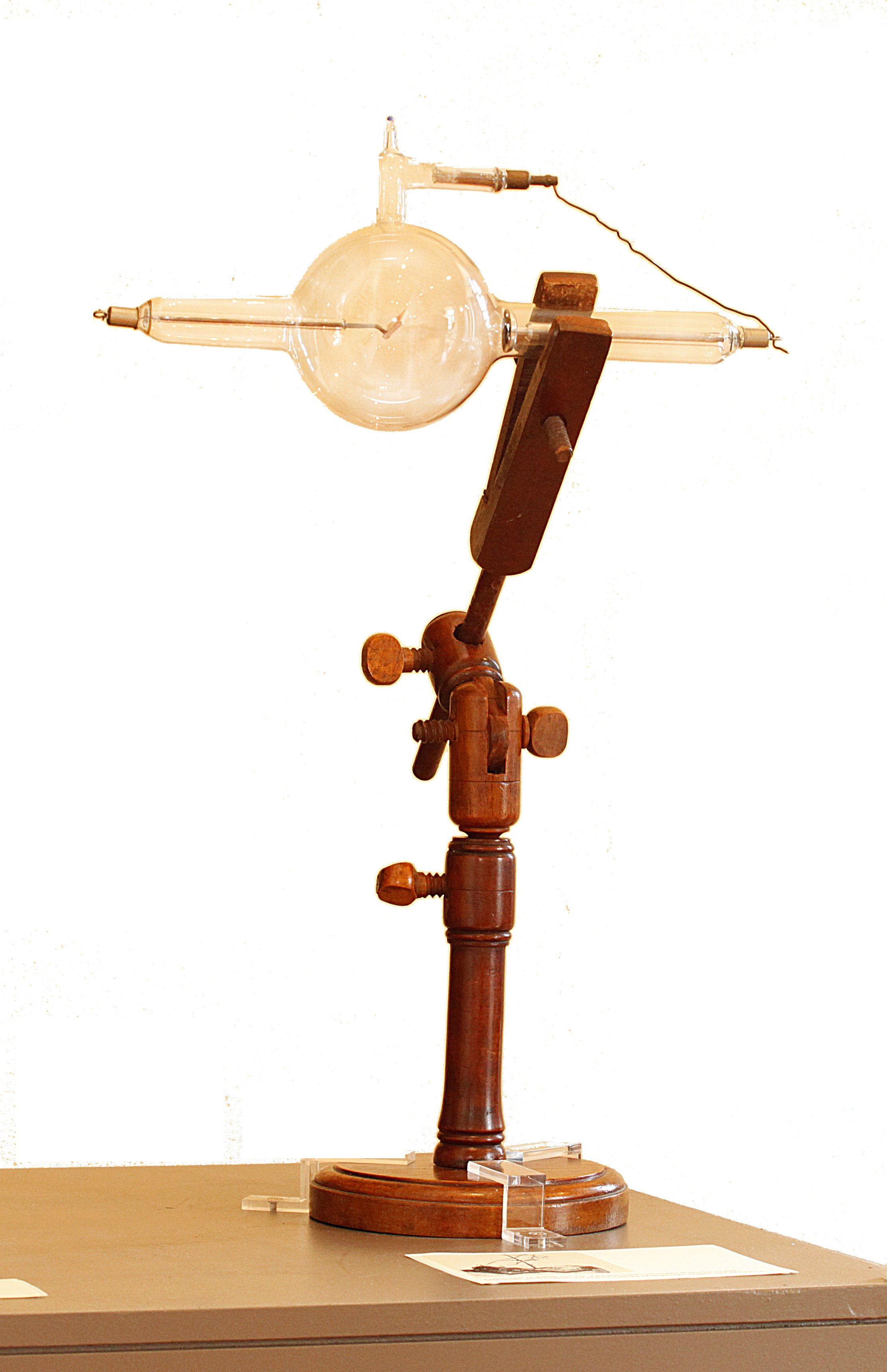
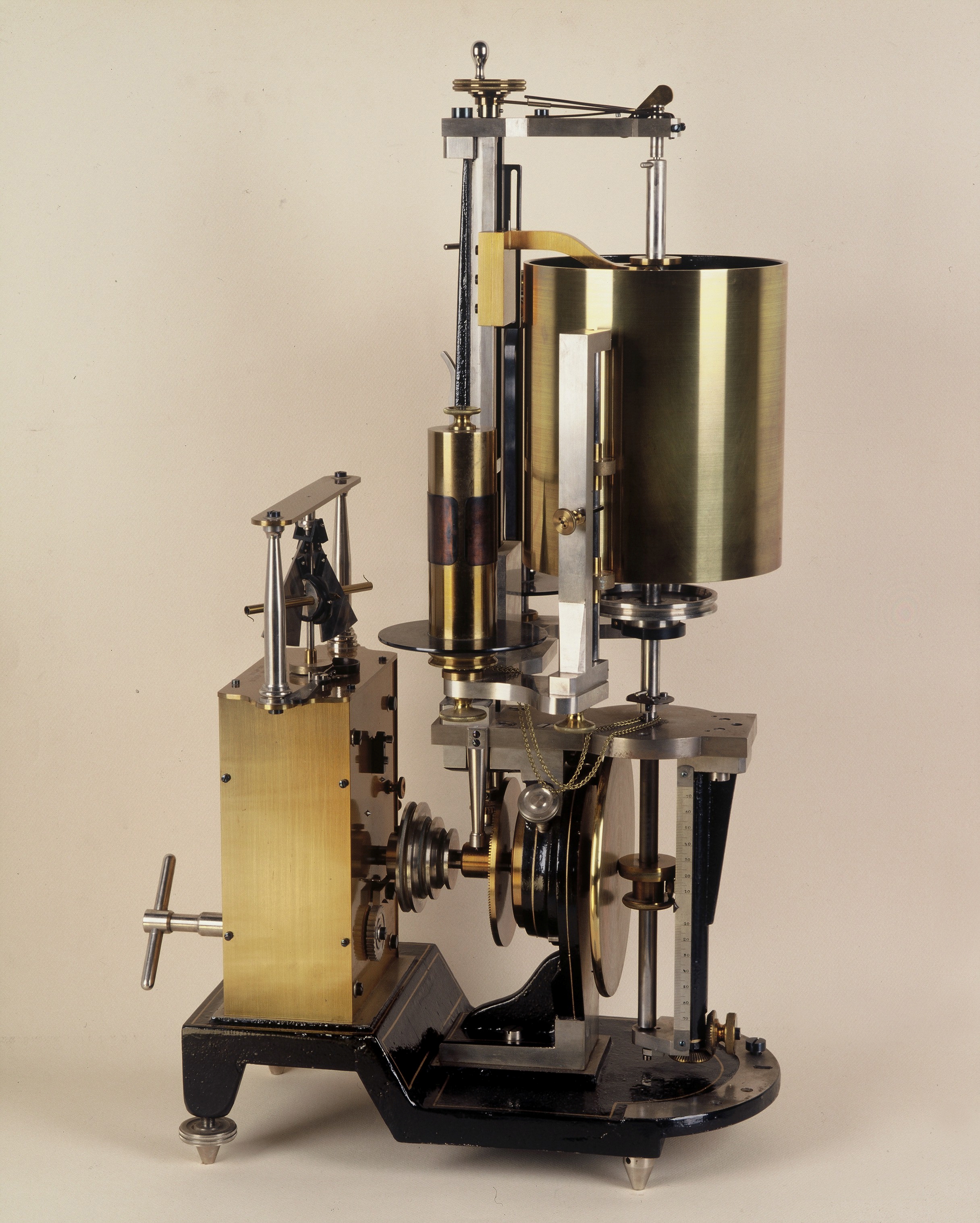
Kymograph or kymography. Medical instrument for recording blood pressure which has been widely used in experimental psychology, as well, early 20th century. Manufacturer: E. Zimmermann, Leipzig, Germany.
Athens University History Museum.
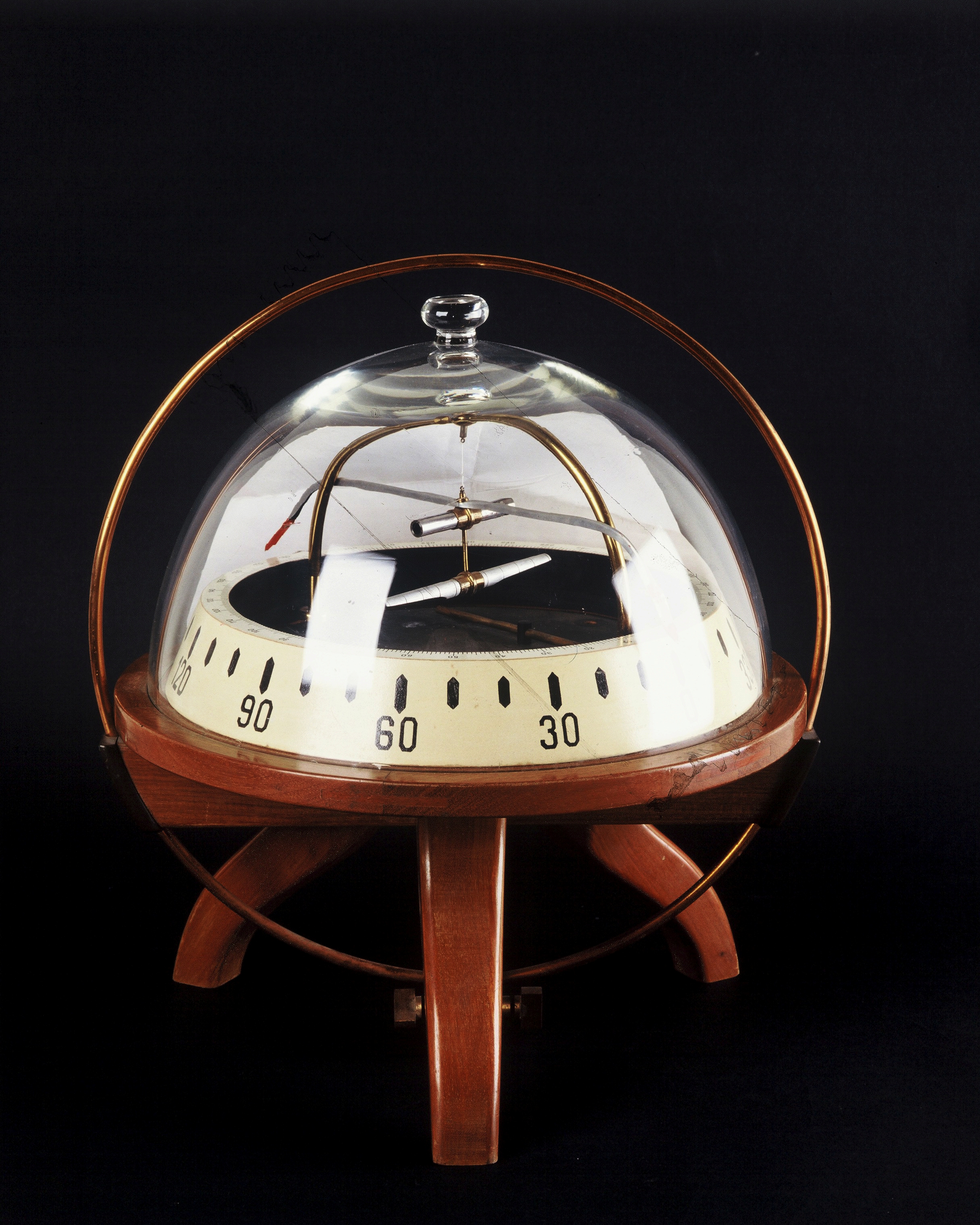
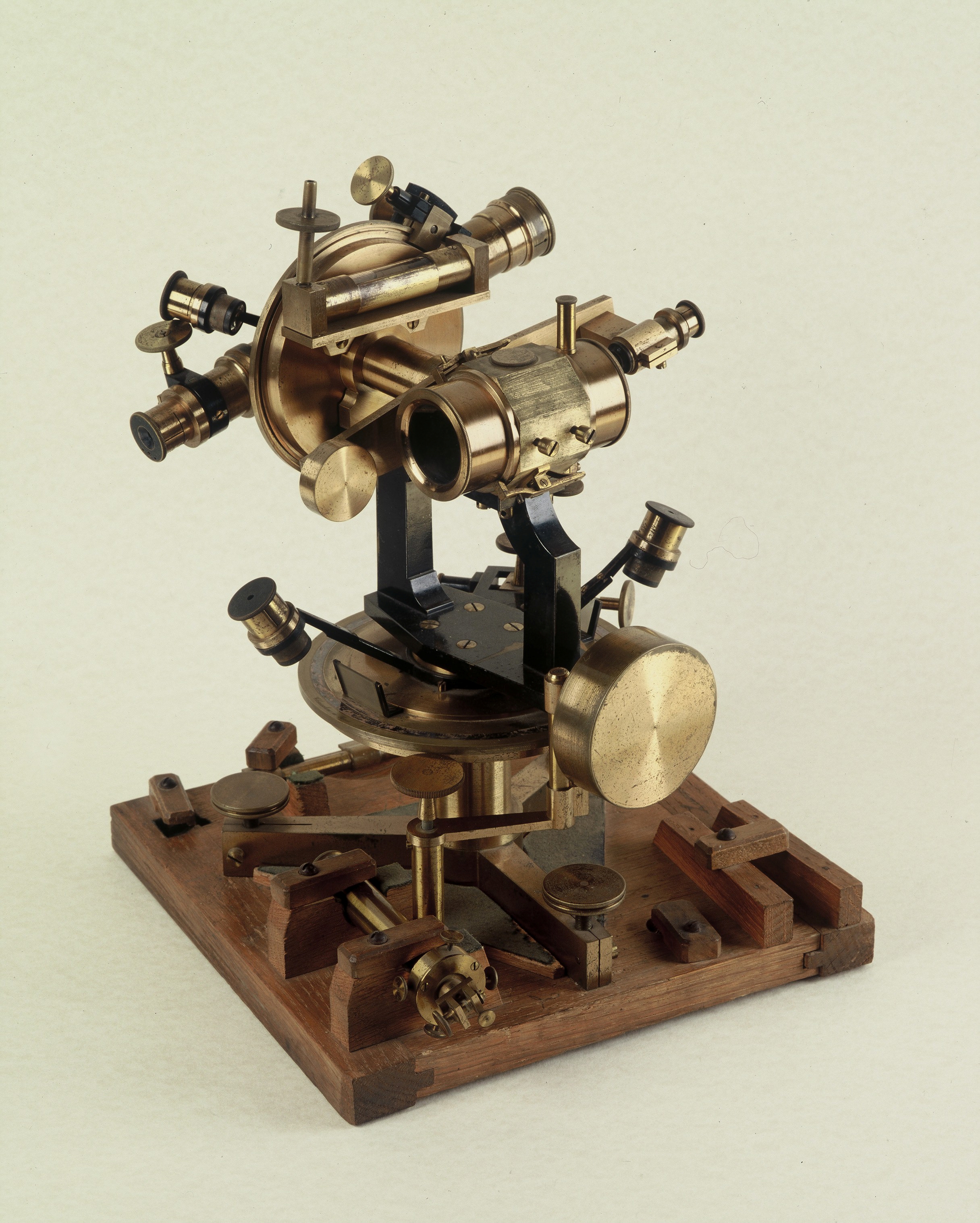
Theodolite. Portable instrument used in astronomy and topography to measure angles in vertical and horizontal planes, first half of the 20th century. Manufacturer: Chasselon, Paris.
Athens University History Museum.
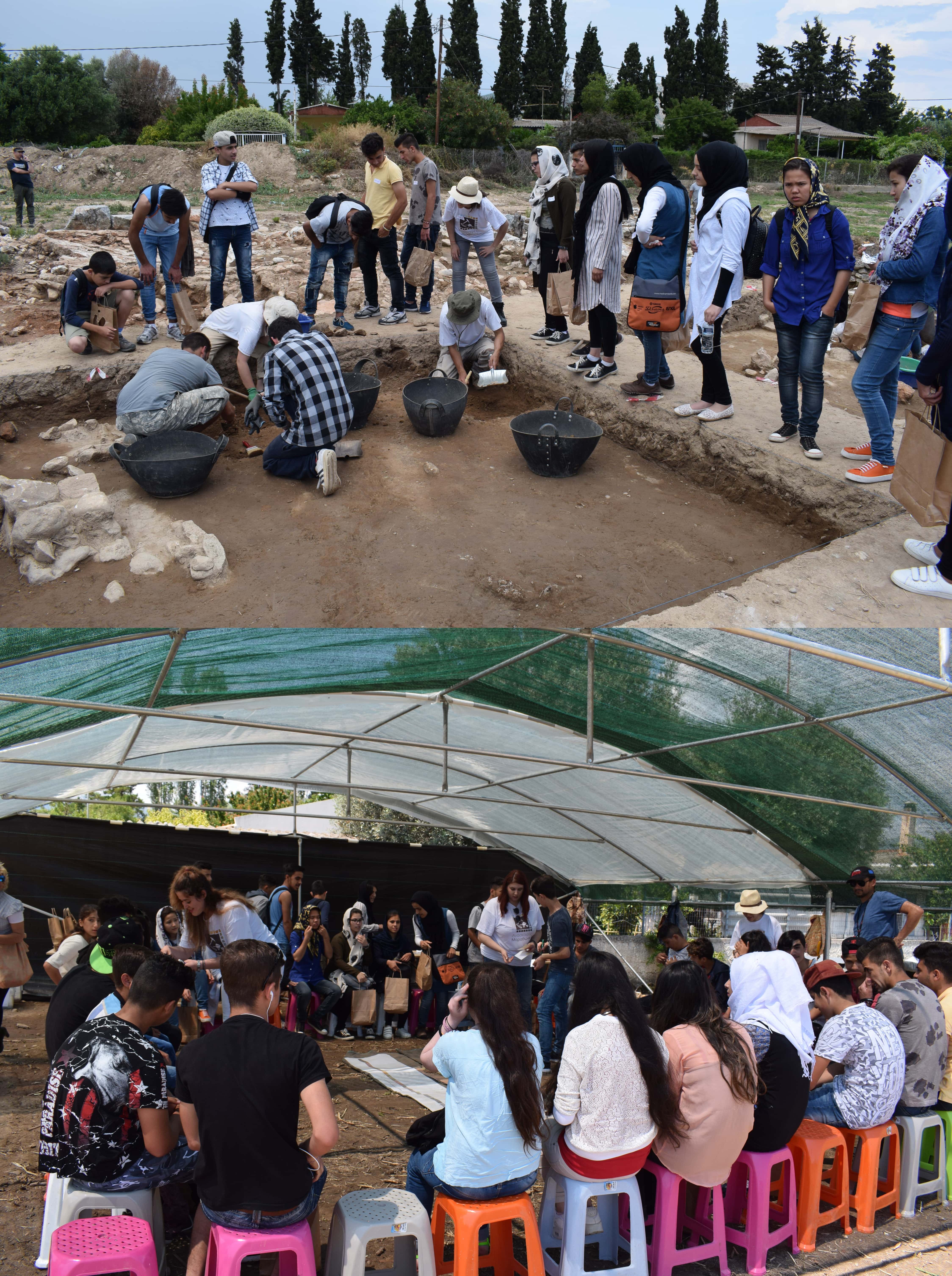
Photographs from the visit of refugees from the hospitality facilities of Skaramangas to the university excavation in Plasi, Marathon, May 2017.
Department of Archaeology and History of Art, Department of History and Archaeology «School of Philosophy, University of Athens».
The Histology-Embryology Laboratory of the Department of Medicine of the School of Health Sciences.
School of Health Sciences, University of Athens.
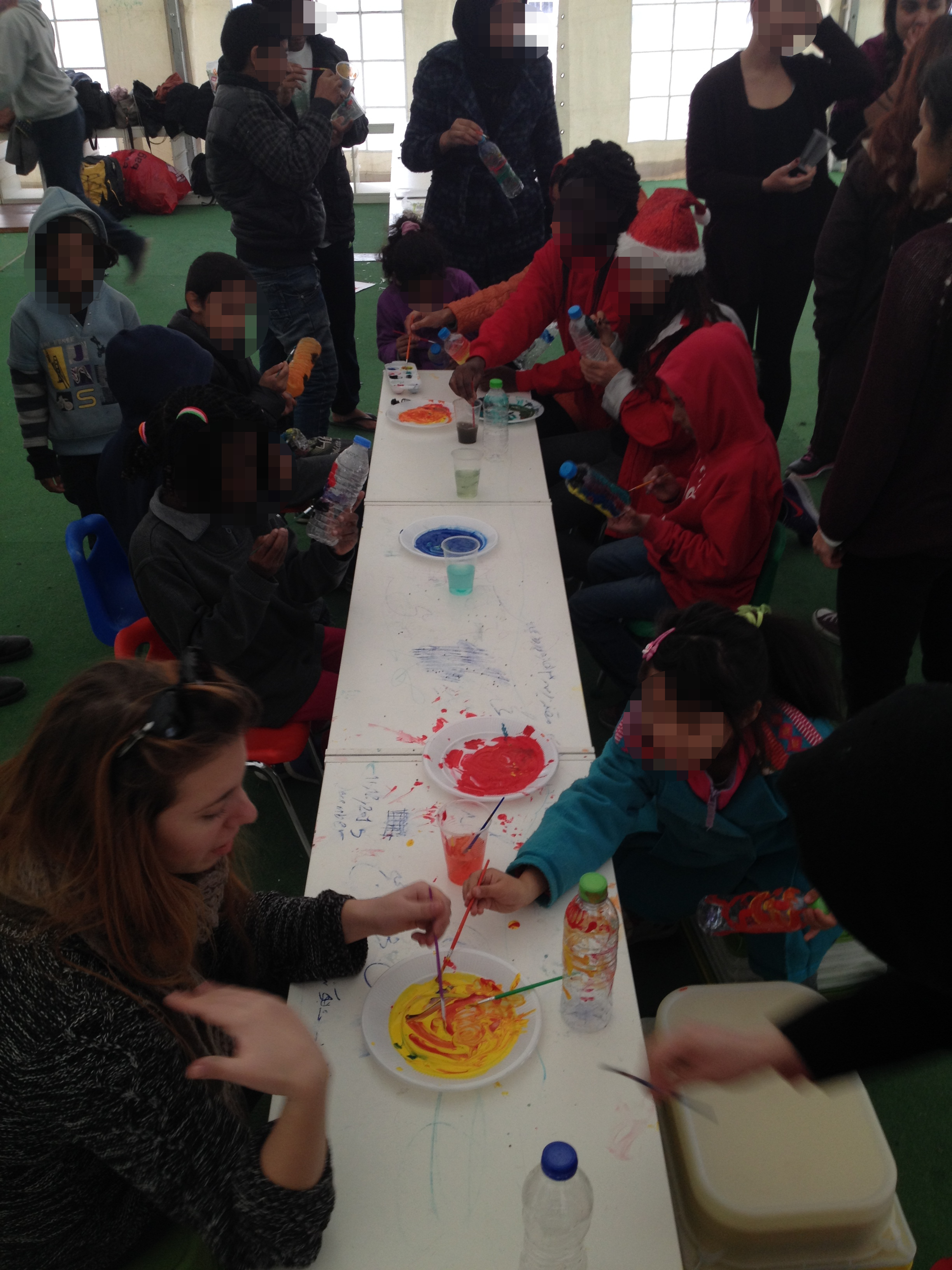
A group of students from the Department of Education and Early Childhood Education organizes educational interventions twice a week at the Open Hospitality Facility of Eleonas, November 2015.
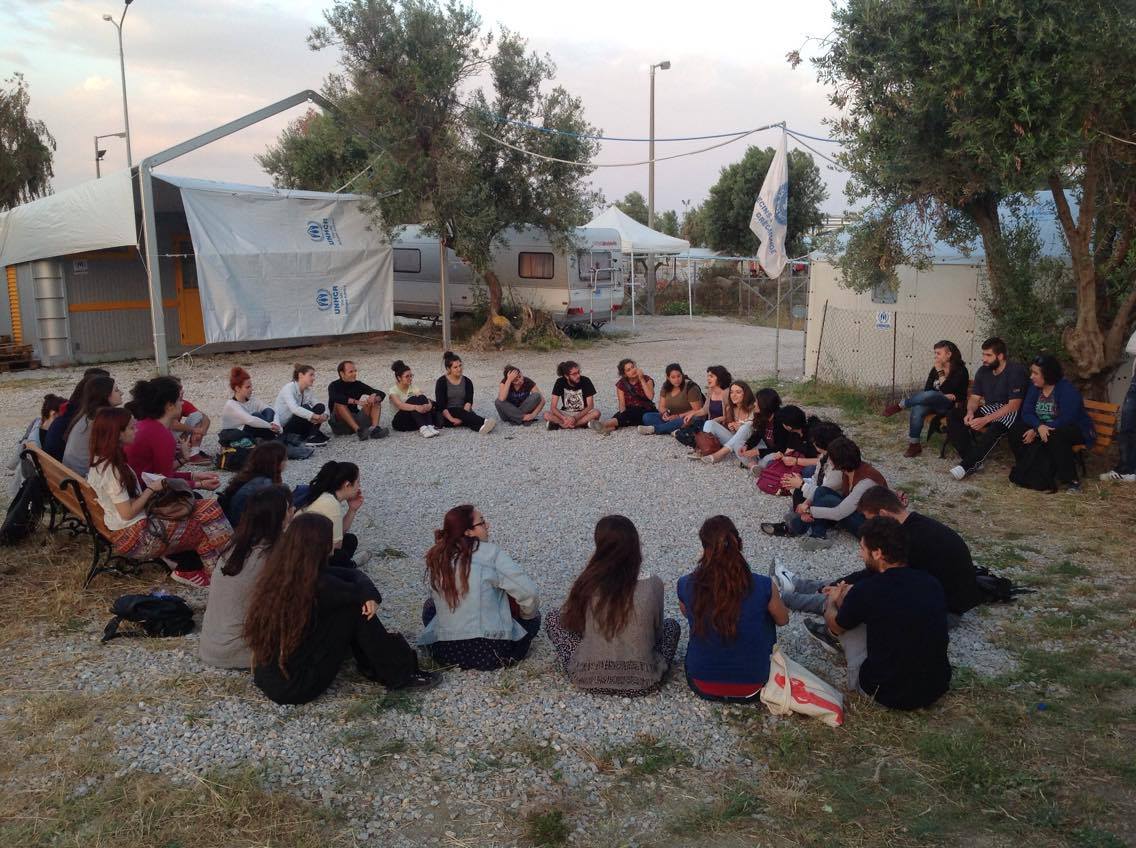
The intervention team of the Athens University Department of Early Childhood Education trains students of the Department of History and Social Anthropology of the University of the Aegean in organizing educational interventions for refugee children in Kara Tepe-Mytilini, March 2016.
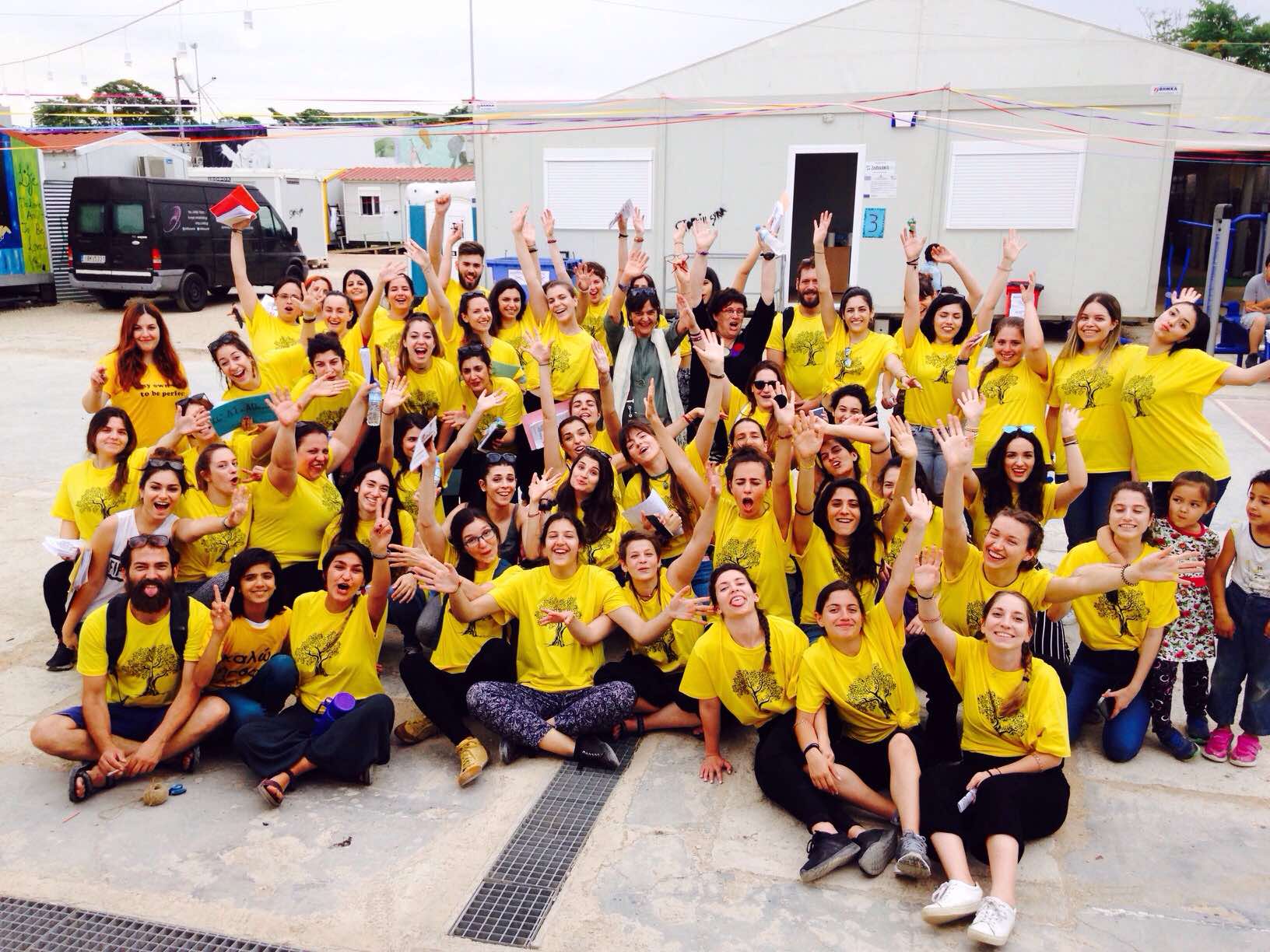
«Elaionas-Olive Grove Festival» with the participation of students from the surrounding schools. The Intervention Team of the Athens University Department of Early Childhood Education supports the festival and eagerly participates in the activities that have been planned.
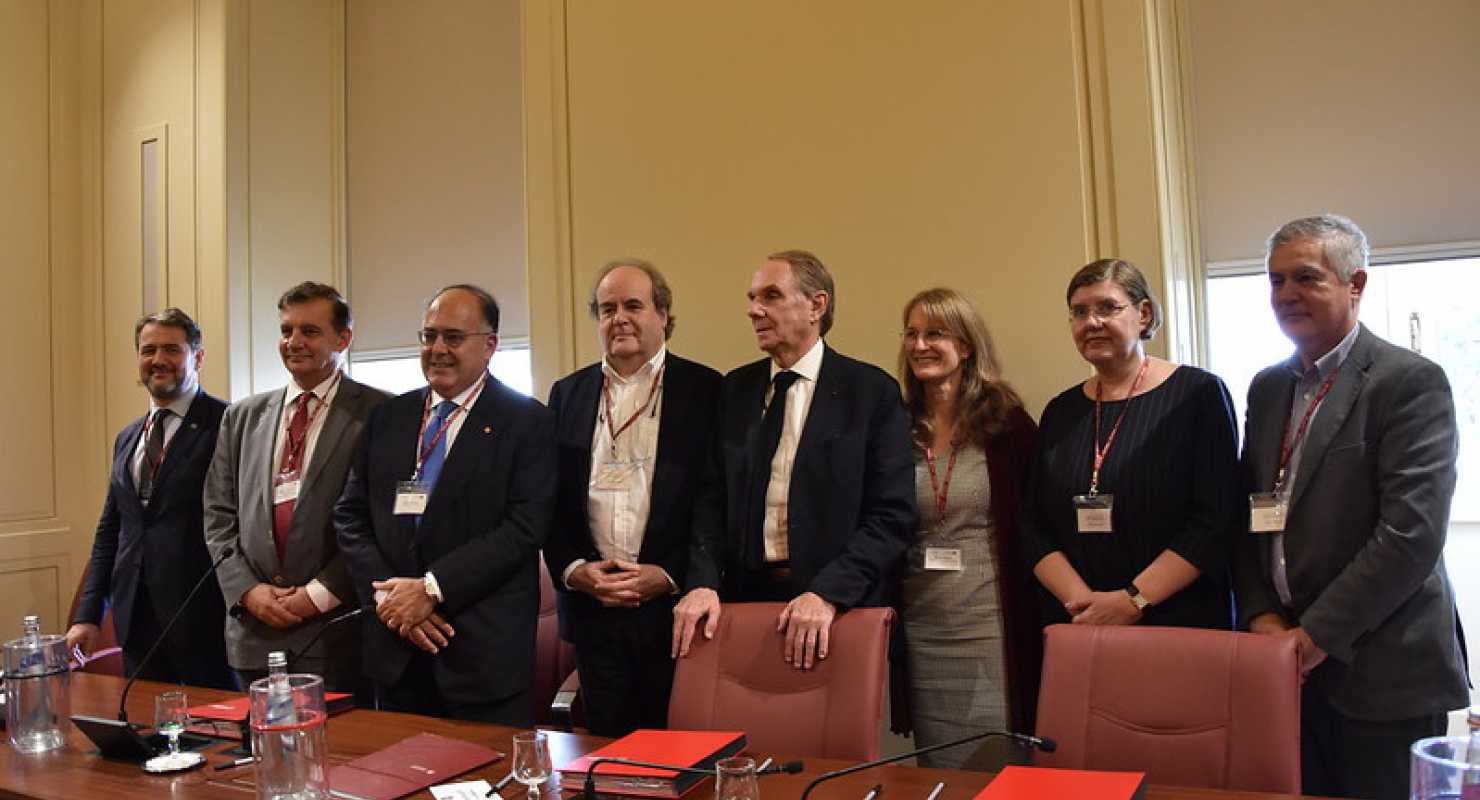
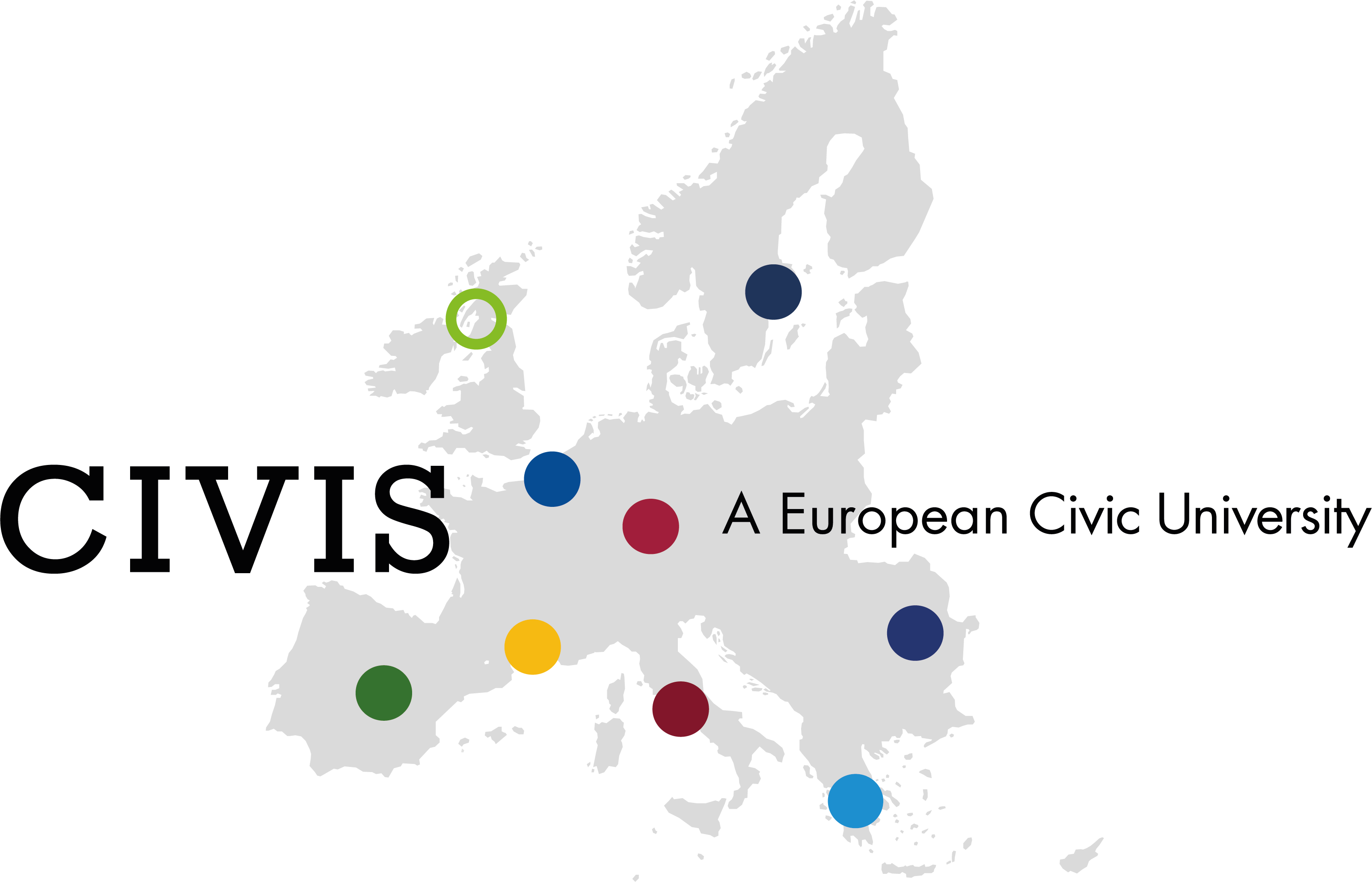
The National and Kapodistrian University of Athens participates in the European Civis University (European University CIVIS/ civis.eu/en ) in the framework of the initiative for the establishment of the European Universities of the European Commission. Nine universities participate in the European Civis University, the Aix-Marseille Université, the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Universitatea din București, Université libre de Bruxelles, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Sapienza Università di Roma, Stockholm University and Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen and the University of Glasgow.
The National and Kapodistrian University of Athens participates in the European Civis University (European University CIVIS/ civis.eu/en ) in the framework of the initiative for the establishment of the European Universities of the European Commission. Nine universities participate in the European Civis University, the Aix-Marseille Université, the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Universitatea din București, Université libre de Bruxelles, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Sapienza Università di Roma, Stockholm University and Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen and the University of Glasgow.